Gynecology
In the field of gynecology, we offer comprehensive preventive examinations, treatment of gynecological diseases, menopause, diagnosis and treatment of infertility, as well as contraceptive counseling, including those based on natural methods.
Control gynecological visit
During a routine control visit, basic tests are performed, i.e. gynecological examination with vaginal ultrasound, breast ultrasound and cytology.
It is possible to perform additional tests, i.e .:
- LBC liquid cytology,
- collection of material for microbiological tests from the vagina, including an extended urogenital panel performed using the PCR method,
- testing for sexually transmitted diseases,
- tests for the detection of HPV,
- other imaging tests, including thyroid ultrasound,
and prophylactic vaccination against cervical cancer.
Read about:
When should you seek advice from a gynecologist-obstetrician?
Every woman should visit a gynecologist prophylactically once a year, and also when disturbing symptoms appear, such as:
- abnormal vaginal bleeding
- unpleasant vaginal smell,
- abnormal vaginal discharge
- itching, burning intimate parts,
- pains in the lower abdomen area not related to the menstrual cycle,
- irregular, painful, heavy or absent periods
- other disturbing ailments related to the intimate sphere, also of a sexological (psychological) basis.
A woman planning pregnancy should report for consultation preferably three months before starting efforts (a pre-conception visit). Lack of pregnancy after a year of regular efforts requires a detailed diagnosis of a couple trying to get pregnant.
After exhausting the natural methods in supporting reproduction, highly specialized treatment is carried out in clinics in Poland and abroad, based on many years of cooperation.
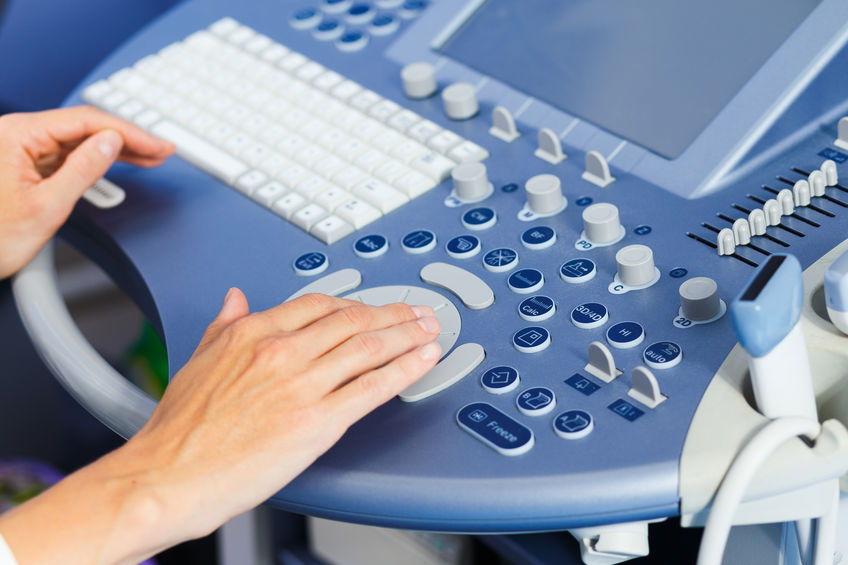


Ultrasound examination (USG) – how to prepare for the examination?
Ultrasound is a diagnostic imaging test, a device that sends an ultrasonic wave is used, which allows you to view the inside of many organs of our body.
Depending on the type of examination, ultrasound is performed in different ways and requires different preparation.
Vaginal (transvaginal) ultrasound
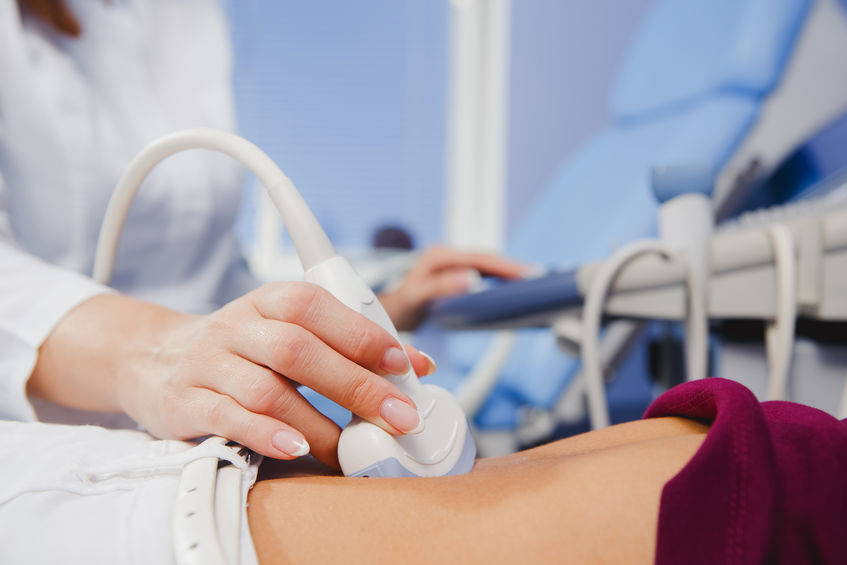
It is the most common additional gynecological examination, both before and during pregnancy, and as a regular preventive examination. It should accompany each gynecological examination because it allows for quick diagnosis of many diseases, e.g. ovarian cysts or uterine fibroids. In early pregnancy, it is the primary confirmatory test. It allows to visualize the embryo already in the 4th week of pregnancy, the heart rate of the embryo from the 6th week of pregnancy. During pregnancy, vaginal ultrasound examining the fetus is performed until the 14th week, and this examination is performed until the end of pregnancy to assess the cervix.
Ultrasound of the reproductive organ through the abdominal wall.
It is performed in special cases, in girls and women who have not had intercourse. It is performed lying down. The doctor covers the patient’s skin with the gel. Then he moves the head of the apparatus over the examined organs. The image showing the reproductive organ – uterus, ovaries is visible on the screen and recorded on paper.
This examination takes approximately 15-20 minutes.
Preparation for the test:
In order for the test to be performed correctly, remember that the patient’s bladder must be full (it is recommended to drink 2-3 glasses of fluids about 2 hours before the test)
HSG-USG (Sonohisterosalpingographia)
It is a fallopian tube patency test. It involves the administration of a physiological saline solution into the uterine cavity through a sterile catheter. Using vaginal ultrasound, the doctor assesses whether the administered fluid flows out of the fallopian tubes and thus assesses their patency. The examination also assesses the shape and size of the uterus, the passage of fluid through the fallopian tubes and its spread between the loops of the intestines.
Preparation for the test:
Two days before the procedure, immediately after the menstrual period, take an antibiotic orally prescribed by a doctor, and two hours before the procedure, take painkillers and diastolic medications. Before the procedure, a gynecological consultation and a current Pap smear are required.
The test takes about 30 minutes.
Pap smear – standard
It is a screening test to detect both precancerous conditions and cervical cancer.
Due to the high effectiveness of the cytological test in detecting many diseases of the genital tract, it should also be remembered before a planned pregnancy.
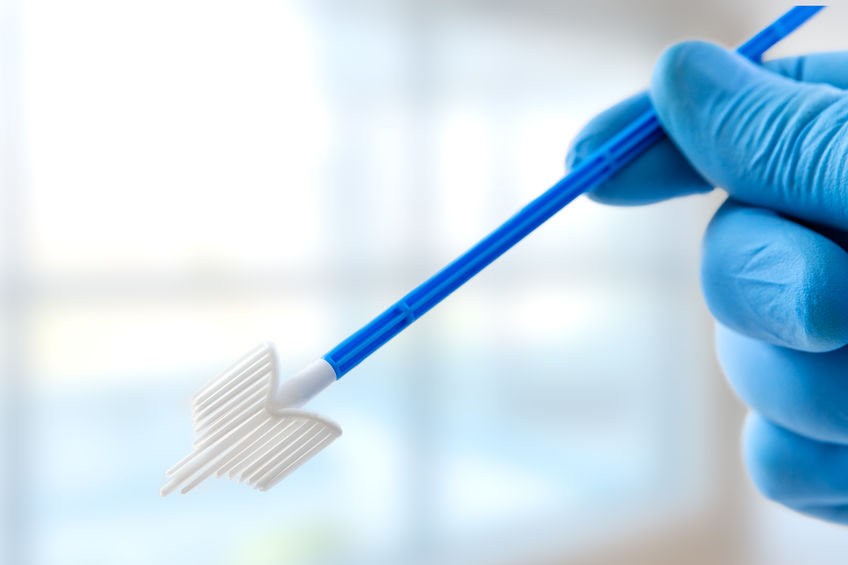


Liquid cytology (LBC) – recommended
It is a thin-layer cytology on the LBC (Liquid Based Cytology), a new technique of screening for cervical cancer. Compared to traditional cytology, it is more sensitive and more accurate.
In this method, a cervical swab is collected on a special liquid medium, not on a slide. This substrate minimizes the risk of cell damage and allows to eliminate undesirable elements from the collected material, i.e. mucus, red and white blood cells, and bacteria that make further microscopic evaluation difficult. Currently, it is recommended to extend liquid cytology to HPV DNA typing, especially in women whose standard cytology results were abnormal.
The method of performing the test:
Material for cytological examination is collected during a routine gynecological examination. The collection itself consists in making a swab of the vaginal part, disc and cervical canal with a special brush (cytobrush), and then smearing the collected material on a slide, which is submitted for microscopic evaluation by a specialist.
It should be remembered that the Pap smear test is painless.
Preparation for the test:
The material for the cytological examination is collected before a gynecological examination, vaginal ultrasound examination and other examinations of the vagina and / or cervix, e.g. taking culture. Pap smear can be performed at any time during the cycle, excluding the days of menstruation.
No vaginal medications / preparations, tampons or irrigation (vaginal irrigation) should be used 48 hours before the examination. At least 24 hours before the examination, you should not have sexual intercourse, do not undergo a gynecological examination, transvaginal examination, ultrasound examination, and no cultures or swabs from the cervical canal.
In the event of inflammation of the reproductive organ (it can be evidenced by, for example, vaginal discharge), you should first cure the inflammation and then report for the examination.
Waiting time for the Pap smear results: 14-21 days